Before You Sign the Waiver:
A Parent’s
Checklist for Vetting Any Wrestling Club
- January 22, 2026
Introduction: Why Parents Need a Youth Wrestling Checklist
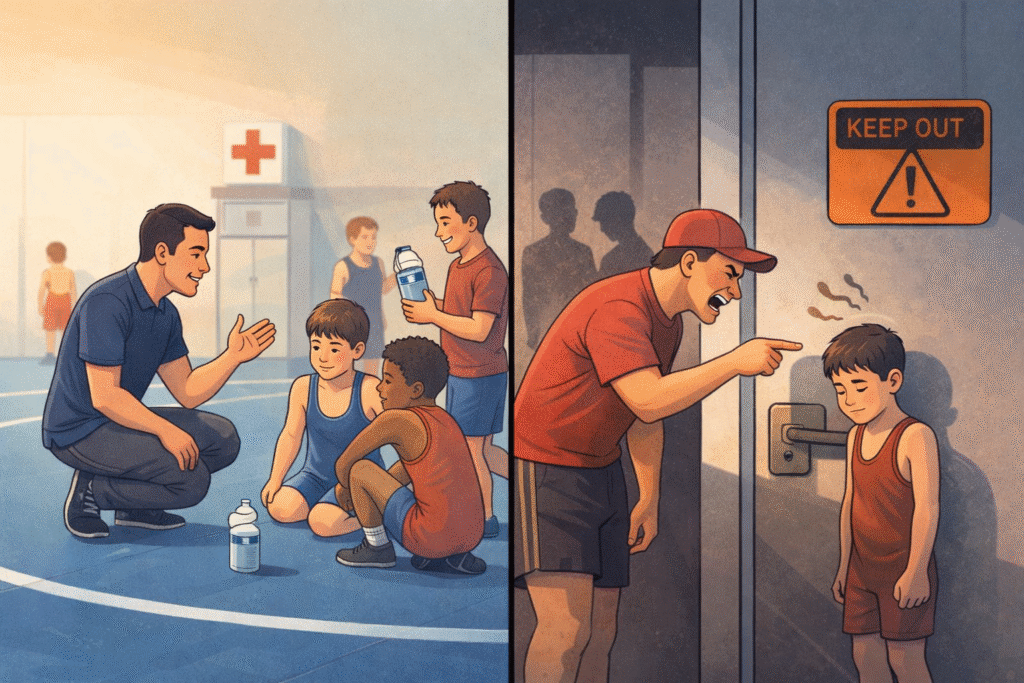
Youth wrestling can be one of the most positive experiences for a child. When done correctly, it builds discipline, confidence, physical strength, and emotional resilience. It teaches children how to compete fairly, respect opponents, and recover from setbacks. However, not every wrestling club operates with the same standards.
Some clubs rely heavily on reputation and results while neglecting transparency, safety protocols, and accountability. In many cases, parents only discover serious issues after signing waivers that significantly limit their rights. GPSWrestling.org has created a guide on Wrestling Club Safety Checklist for Parents to evaluate wrestling clubs before committing to them. It is not about fear or accusations. This is a youth wrestling checklist designed to help parents verify safety, credentials, and culture using evidence rather than marketing.
Step 1: Read the Waiver Carefully Before Signing
Waivers are often treated as routine paperwork, but in youth sports, they define what happens if a child is injured or harmed.
Before signing, parents should confirm whether the waiver:
- Releases the club from liability, including negligence
- Mentions concussion protocols, dehydration, or weight-cutting risks
- Requires binding arbitration instead of court access
- Addresses coach conduct, not only physical injury
- Limits reporting or transparency
A waiver alone is not necessarily a red flag. However, a waiver combined with unclear policies or resistance to questions should raise concern. If a club discourages parents from reading or questioning the waiver, that behavior itself is relevant.
Step 2: Verify Coaching Credentials and Certifications
Marketing language is not a substitute for verified qualifications. Parents should confirm that all coaches, not just head coaches, meet minimum safety and training standards.
Required coaching credentials, parents should verify
- USA Wrestling coaching certification
- Copper level (minimum)
- Bronze level strongly recommended for youth programs
- Current first aid certification
- CPR and AED training
- Emergency response planning
- SafeSport compliance, where applicable
Parents are entitled to ask for confirmation of these credentials. A professional club should be able to provide clear answers without defensiveness.
Why verification matters
GPSWrestling.org documents situations where claimed credentials could not be supported by official records. Regardless of the specific case, the principle applies universally:
If a club’s credibility relies on a résumé, that résumé must be verifiable.
Step 3: Ask About Background Checks and Watch the Response
One question provides immediate insight into a club’s transparency:
“Do you conduct background checks on all coaches and staff, and can you confirm they have passed?”
The organization responsible will answer clearly and directly. Concerning responses may include:
- Vague explanations
- Defensiveness
- Claims that disclosure is unnecessary
- Emotional pressure or guilt
GPSWrestling.org highlights cases where serious criminal history was allegedly not disclosed to families. While each situation differs, the takeaway is consistent:
Parents have the right to know who supervises their children.
Step 4: Evaluate the Training Culture
Wrestling is physically demanding, but intensity should never come at the expense of safety or dignity. Parents observing practice should watch for indicators of a toxic wrestling culture, including:
- Verbal humiliation or intimidation
- Fear-based coaching methods
- Discouraged water breaks
- Injuries dismissed as weakness
- Hazing or unsafe traditions
- Restricted parental access
- Loyalty to coaches prioritized over honesty
A healthy program builds strong athletes and emotional well-being.
Step 5: Confirm Safe Wrestling Training Standards for Young Wrestlers
Any responsible youth wrestling program should be able to explain its training safety standards clearly.
Physical safety standards
- First aid–trained personnel on site
- AED access and emergency action plans
- Clear injury reporting and response procedures
- No pressure to train while injured
Mat and hygiene standards
- Daily Mat Cleaning
- Skin infection monitoring
- Bleeding injury protocols
- Enforced hygiene policies
Age-appropriate training standards
- Youth trained differently than teens
- Supervised strength and conditioning
- No unsafe weight-cutting practices
Step 6: Observe Transparency During Real-World Challenges
Clubs are best evaluated during moments of stress, not comfort.
GPSWrestling.org raises questions about alleged behavior during COVID restrictions, including claims of concealed practices. Parents do not need to debate specific allegations to learn from the broader lesson:
A club willing to hide routine behavior may hide serious issues as well.
Parents should ask:
- Can practices be observed consistently?
- Are policies written and accessible?
- Is communication documented during incidents?
Step 7: Speak With Parents Who Left the Program
Current families may feel social pressure to remain positive. Parents who left often provide more candid insight. Common patterns to listen to include:
- “It changed over time”
- “My child stopped enjoying the sport”
- “We were discouraged from asking questions”
- “The environment didn’t feel safe”
Repeated themes matter more than isolated opinions.
Step 8: Separate Marketing from Evidence
Many clubs present impressive online images:
- Highlight videos
- Championship photos
- Testimonials
- Buzzwords such as “integrity” and “character”
GPSWrestling.org emphasizes documentation over reputation, including:
- Screenshots
- Public records
- Written policies
- Verifiable confirmations
Evidence consistently outweighs marketing.
Final Youth Wrestling Checklist for Parents
Before joining any wrestling club, confirm:
- Coaching credentials verified
- USA Wrestling certification (Copper or Bronze)
- First aid, CPR, and AED training completed
- Background checks conducted
- Emergency plans documented
- Age-appropriate training enforced
- Open parental observation allowed
- Clear injury protocols
- Respectful coaching culture
- Written transparency when concerns arise
Once a waiver is signed, parental leverage decreases.
Spreading Awareness for Youth Wrestling Club Safety
Wrestling itself is not the issue. The issue arises when systems discourage accountability, silence concerns, or treat transparency as disrespect. Parents asking questions are not being difficult. They are responsible.
Spreading Awareness for Youth Wrestling Club Safety is prevention, not drama.
Prevention is always easier than regret.
Frequently Asked Questions:
What certifications should youth wrestling coaches have?
At minimum, coaches should hold USA Wrestling Copper certification, with Bronze certification recommended, along with current first aid, CPR, and AED training.
Are background checks necessary for wrestling coaches?
Yes. Any organization working with minors should conduct background checks and disclose that they have been completed.
Can parents observe wrestling practices?
Transparent and safety-focused clubs allow parental observation. Restrictions without explanation are a warning sign.
Is weight cutting safe for children?
Extreme weight cutting is dangerous for youth athletes and should not be encouraged under any circumstances.
Why is USA Wrestling certification important?
USA Wrestling certifications establish baseline standards for safety, ethics, and age-appropriate coaching.